

This means that two electrons are involved in chemical bonding, and that these electrons move through an orbital, or range of probabilities, roughly corresponding to a sphere. (By contrast, the core electrons, which occupy lower regions of energy within the atom, play no role in the bonding of elements.)Īll members of the alkaline earth metal family have a valence electron configuration of s 2.
Valence electrons -the electrons at the "outside" of the atom, involved in chemical bonding. All elements in a particular group, regardless of their apparent differences, have a common pattern in the configuration of their With the advances in understanding that followed the discovery of the electron in 1897, along with the development of quantum theory in the early twentieth century, chemists developed a more fundamental definition of family in terms of electron configuration.Īs noted, the alkaline earth metal family occupies the second group, or column, in the periodic table. These properties will be discussed with regard to the alkaline earth metals, but another point should be stressed in relation to the division of elements into families. Where families are concerned, there are certain observable properties that led chemists in the past to group the alkaline earth metals together. ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS OF THE ALKALINE EARTH METALS. Metals also form ionic bonds, the tightest form of chemical bonding. For instance, metals, which comprise the vast majority of elements on the periodic table, tend to be shiny, hard, and malleable (that is, they can bend without breaking.) Many of them melt at fairly high temperatures, and virtually all of them vaporize (become gases) at high temperatures. These groupings, both in terms of family and the broader divisions, relate both to external, observable characteristics, as well as to behaviors on the part of electrons in the elements' atomic structures. (These are also discussed in separate essays, which include reference to "orphans," or elements that do not belong to one of the families mentioned above.) (All of these are covered in separate essays within this book.) In addition, there are several larger categories with regard to shared traits that often cross family lines thus all elements are classified either as metals, metalloids, and nonmetals. These include (in addition to the alkaline earth metals and the alkali metals) the transition metals, halogens, noble gases, lanthanides, and actinides. The expression "families of elements" refers to groups of elements on the periodic table that share certain characteristics. Radium, on the other hand, is rarely used outside of laboratories, in large part because its radioactive qualities pose a hazard to human life. Barium and beryllium have numerous specialized applications in areas from jewelry to medicine, while strontium is primarily used in fireworks. In fact, both are significant components in the metabolism of living things -including the human body. Magnesium and calcium have a number of uses, ranging from building and other structural applications to dietary supplements. Also, like the alkali metals, or indeed any other family on the periodic table, not all members of the alkali metal family are created equally in terms of their abundance on Earth or their usefulness to human life.
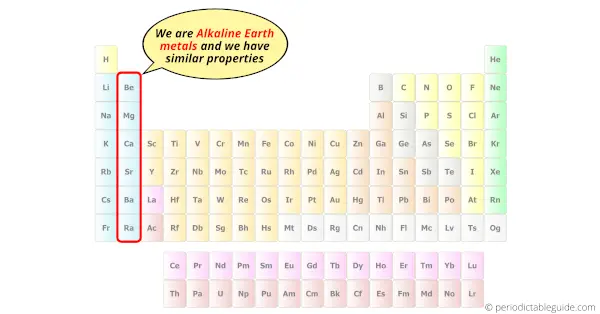
This puts them beside the alkali metals in Group 1, and as their names suggest, the two families share a number of characteristics, most notably their high reactivity. The six alkaline earth metals -beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium -comprise Group 2 on the periodic table of elements.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
